Anomaly detection with isolation forest
In this experiment, we use an isolation forest to detect heartbleed traffic flows.
About isolation forest
Isolation forest is described in some detail in (1, 2). Using isolation forest, one can separate out data points that are different along some feature dimensions from the rest of the data points. Isolation forest works by recursively partitioning the training dataset till each point in the dataset is isolated. Subsequently, test samples are scored using the partition structure created during training. Test samples that have a score beyond a pre-determined threshold are deemed anomalies.
Experimental results for heartbleed
The heartbleed attack class has just 11 samples in the raw data. We set up a new dataset with these 11 samples and 8000 samples from the BENIGN class (3). We use 7989 of the BENIGN samples to train Scikit-learn’s isolation forest. Subsequently, we feed the 11 attack samples and the 11 BENIGN samples to the algorithm. We see that isolation forest returns an accuracy of 91% with a false positive rate of 9% (4).
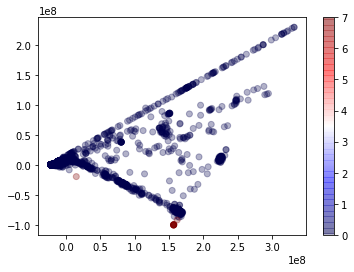
A plot of the labels against the first two principal components (from a principal component analysis) indicates why isolation forest can detect the heartbleed traffic flows as anomalies. We see that heartbleed samples are mostly separated from BENIGN data. However, we do observe some BENIGN data points close to heartbleed data points. This proximity is likely responsible for false positives.
Principal components one, two
Trying isolation forest with portscan
We try isolation forests with the two-class dataset created for a previous experiment (5). This dataset contains only BENIGN, and portscan traffic flows. Isolation forest returns an accuracy of just 41%, with false positives accounting for 9% and false negatives for 50% (multiple runs do not change the result).
We know that portscan traffic flows are not distinguishable from BENIGN traffic on principal component plots from prior experimentation. Given this previous result, we can understand why isolation forest does not work well on the two-class dataset: the attack traffic is not sufficiently distinct from BENIGN traffic.